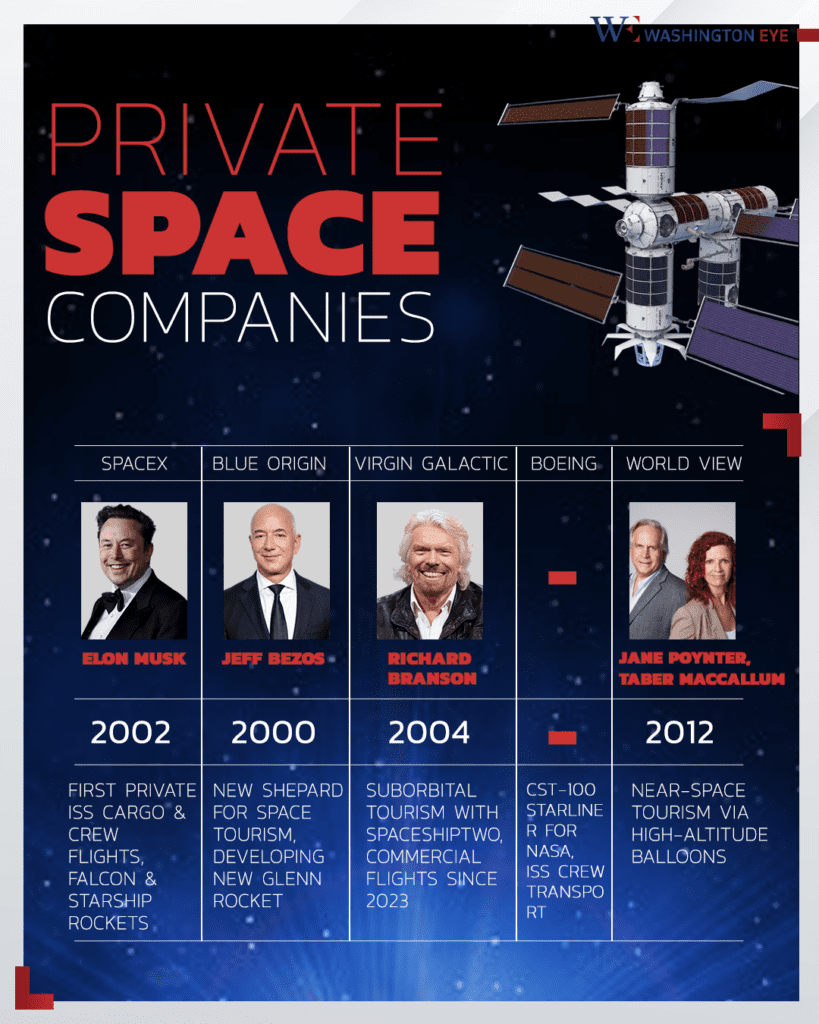
The face of space exploration is undergoing a historic transformation as private sector leadership takes center stage in reshaping NASA’s future. In a groundbreaking move, the U.S. government has approved a significant shift toward privatizing space operations, allowing billionaire entrepreneurs to play an influential role in directing the agency’s strategic goals.
The decision has sparked widespread debate over the implications of corporate-driven space exploration, raising questions about the balance between public interests and commercial incentives. The Biden administration announced last year the appointment of SpaceX’s CEO Elon Musk as an official strategic advisor to NASA. Musk is now even playing a larger role in the U.S. government, under President Donald Trump.
This development comes amid the increasing role of private companies in space missions, with SpaceX, Blue Origin, and other firms successfully executing projects that were once exclusively NASA’s domain. Musk’s appointment marks the first time a private sector leader has been granted such authority in shaping NASA’s agenda
The decision was unveiled in a joint press conference held at NASA headquarters, where Bill Nelson, NASA Administrator, confirmed that the agency would be undergoing a major structural shift.
“Space exploration is no longer just a government endeavor, it is a joint effort between public and private sectors. Elon Musk’s expertise and contributions in revolutionizing space technology make him an ideal candidate to help shape NASA’s future,” Nelson stated.
Musk, in response, emphasized his vision of making humanity a multi-planetary species. “This is about pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. NASA has done incredible work, but we need to accelerate our ambitions if we want to ensure the survival and expansion of human civilization,” he said.
He also remarked that space travel should not be limited to astronauts and experts but should be accessible to common people as well. Speaking at the press conference on February 3, 2025, Musk added, “We are working towards a future where space travel is as routine as taking a flight, making it possible for ordinary individuals to experience the wonders beyond Earth.”
The Privatization Debate: Progress or Peril?
The shift toward privatization has been met with mixed reactions. While some hail the move as a necessary evolution, critics warn of the risks of handing over space exploration to profit-driven corporations.
Jeff Bezos, founder of Blue Origin and one of Musk’s key competitors, expressed cautious optimism. “This is a critical time for space exploration. While I believe the private sector has a major role to play, we must ensure that commercial interests do not compromise scientific and humanitarian priorities.”
On the other hand, Dr. Lori Garver, former NASA Deputy Administrator, voiced concerns about over-reliance on billionaires. “NASA was founded on principles of scientific advancement and public service. While private sector collaboration is essential, the government must maintain control over decision-making to avoid conflicts of interest.”
Despite these concerns, proponents argue that private investments will accelerate technological advancements and reduce financial burdens on taxpayers. With Musk at the helm, NASA aims to fast-track projects such as the Artemis Program, which plans to return humans to the Moon by 2026, and the ambitious Mars colonization initiative.
What’s Next for NASA?
NASA will rely more on private firms for launch services, satellite deployment, and space station logistics. Companies like SpaceX and Boeing are already managing significant aspects of crewed missions.
Plans to retire the International Space Station (ISS) by 2030 will likely accelerate the development of privately owned orbital stations. With Musk’s involvement, there will be a stronger push toward Mars exploration, potentially leading to the first human settlement on the Red Planet within the next two decades.
Expect a surge in AI-driven missions, with robotic exploration and automated spacecraft playing a central role in upcoming projects.
The privatization shift is also drawing reactions from global space agencies. The European Space Agency (ESA) has expressed interest in deeper collaboration with SpaceX, while China’s National Space Administration (CNSA) has criticized the move as “the commercialization of space for Western dominance.”
Meanwhile, public sentiment remains divided. A recent Pew Research poll revealed that 56% of Americans support the integration of private companies in space programs, while 44% worry about corporate influence overshadowing scientific exploration.
With billionaires like Musk leading the charge, NASA’s trajectory is set for radical transformation. Whether this privatization marks a golden age of innovation, or a corporate takeover of the final frontier remains to be seen.
One thing is certain: the future of space exploration will no longer be defined solely by governments but by the vision and investments of those with the ambition and resources to reach for the stars.