In recent years, strategic decisions from major oil-producing nations have significantly influenced the global energy landscape. Notably, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries and its allies (OPEC+) have implemented a series of production cuts to stabilize oil prices amid fluctuating demand and economic uncertainties. These measures have had profound implications for global energy markets, affecting everything from fuel prices to geopolitical dynamics. In April 2023, OPEC+ announced a voluntary reduction of 1.66 million barrels per day (bpd) in oil production, intended to bolster prices in the face of a potential economic slowdown. This decision was further reinforced in June 2024, when the group extended these cuts through December 2025, maintaining a cautious approach to supply management.
Saudi Arabia, the de facto leader of OPEC, took additional steps by implementing a substantial output cut in July 2024, reducing its production to 9 million bpd from approximately 10 million bpd in May. This marked one of the most significant reductions in recent years, underscoring the kingdom’s commitment to controlling supply to influence market prices.
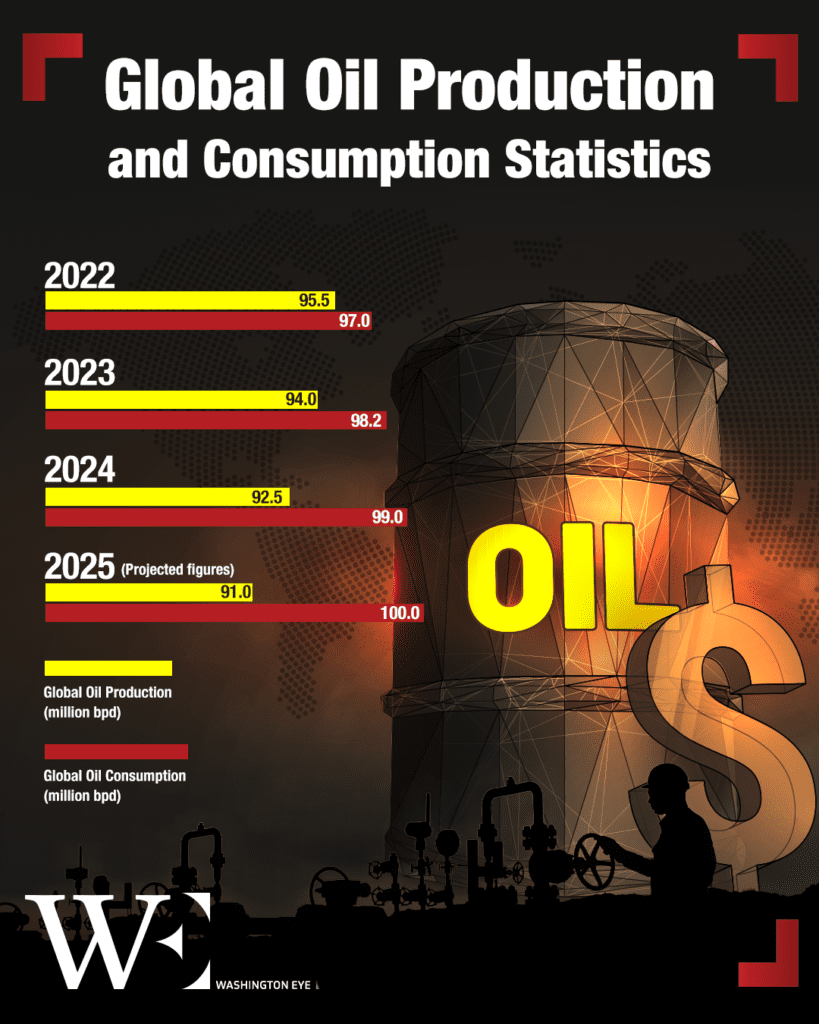
Global Oil Production and Consumption Statistics
To comprehend the full impact of these production cuts, it’s essential to examine recent data on global oil production and consumption. The data indicates a deliberate reduction in production juxtaposed with a steady increase in consumption, leading to a tightening of global oil supplies.
Market Reactions and Price Volatility
The International Energy Agency (IEA) has warned that the extended production cuts by OPEC+ could result in a “significant supply shortfall,” heightening the risk of increased price volatility. In September 2023, the IEA projected a deficit of 1.2 million bpd in the latter half of the year due to these cuts. This supply-demand imbalance has the potential to drive oil prices higher, affecting consumers and economies worldwide.
Despite these supply constraints, global oil prices have experienced periods of decline. As of June 2024, Brent crude, the international benchmark, traded at approximately $81 per barrel, down from $91 in early April. This price movement can be attributed to factors such as record-high U.S. oil output and concerns over sluggish demand in major economies like China.
The strategic production cuts by OPEC+ have not only economic but also geopolitical ramifications. For instance, the United States, a significant consumer of oil, has faced challenges due to these supply constraints. In response, the U.S. government has considered legislative measures, such as the NOPEC (No Oil Producing and Exporting Cartels) bill, which would allow for legal action against OPEC members for market manipulation.
Furthermore, the integration of energy policies with trade agreements has come under scrutiny. The potential imposition of tariffs on Canadian oil imports by the U.S. threatens the longstanding energy partnership between the two nations. Such actions could disrupt supply chains and lead to higher fuel prices in certain regions, exemplifying the complex interplay between energy production decisions and international relations.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the global energy market remains at a crossroads. While OPEC+ continues to manage supply through production cuts, other nations are making strategic investments to bolster their energy sectors. Ecuador, for example, anticipates foreign investments of approximately $42 billion in its oil sector over the next five years, aiming to enhance production amidst declining output.
Similarly, China’s state-owned oil and gas company, CNOOC, has set a new record-high production target for 2025, planning a net production of 760-780 million barrels of oil equivalent, reflecting a 5.6-8.3% increase compared to 2024. These developments indicate a dynamic and evolving energy landscape, where production decisions by key players will continue to shape market trends and economic outcomes globally.
The deliberate production cuts by OPEC+ have had a profound impact on global energy markets, influencing oil prices, economic stability, and geopolitical relations.