In recent years, Bitcoin has emerged as a formidable contender in the financial world, earning the moniker “The New Gold.” With its decentralized nature, scarcity, and growing adoption, Bitcoin has captured the attention of tech enthusiasts and drawn interest from investors, businesses, and governments worldwide. As the world inches closer to a cashless society, Bitcoin’s role in shaping the future of digital payments has become increasingly evident.
Launched in 2009 by the pseudonymous creator Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin was envisioned as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system operating independently of traditional financial institutions. Over the past decade, it has evolved from an obscure cryptocurrency to a global phenomenon. Bitcoin’s market capitalization, which exceeded $1 trillion during its peak in 2021, is a testament to its growing influence. As of January 2025, Bitcoin’s market cap is approximately $520 billion, making it the largest cryptocurrency by far.
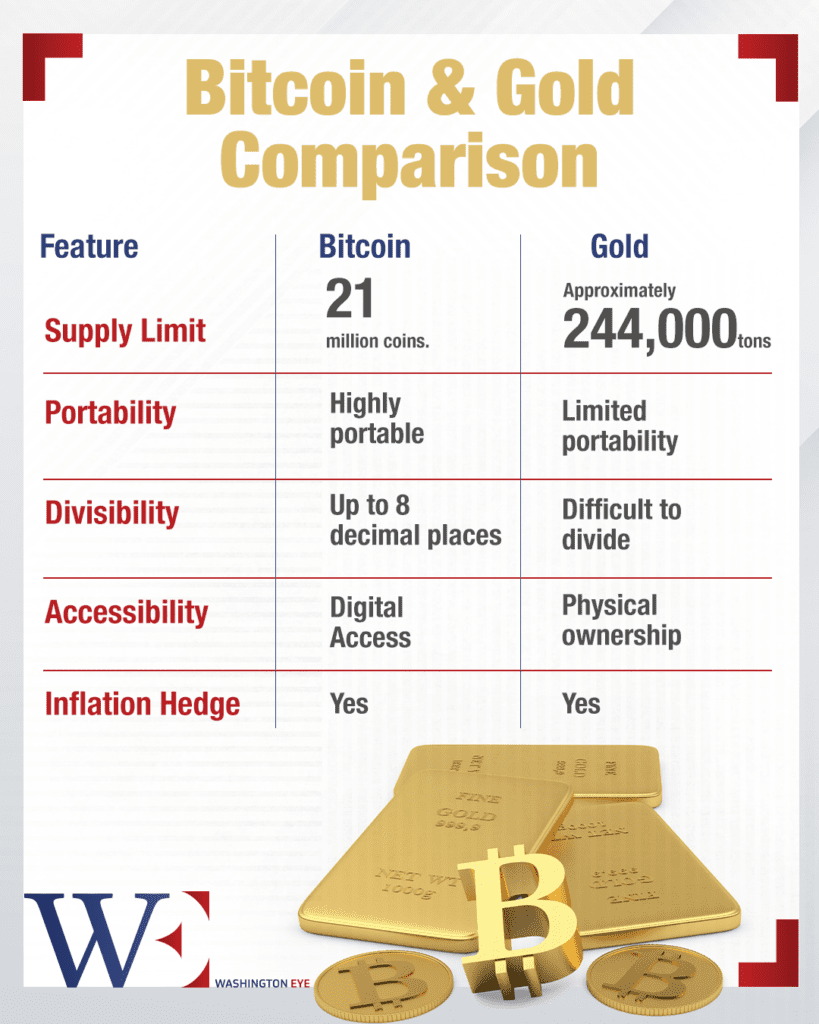
Bitcoin vs. Gold: A Digital Alternative
Historically, gold has been considered a reliable store of value, particularly during times of economic uncertainty. However, Bitcoin is increasingly being referred to as “digital gold” due to its similarities to the precious metal. Both are finite in supply, with Bitcoin’s cap set at 21 million coins, and both are seen as hedges against inflation and economic instability.
While gold requires physical storage and transportation, Bitcoin exists entirely in the digital realm, making it easier to transfer and trade across borders. Moreover, its divisibility allows users to transact in fractional amounts, broadening its accessibility. Bitcoin’s primary use case remains digital payments. Unlike traditional banking systems that involve intermediaries, Bitcoin transactions occur directly between users, reducing fees and processing times. This
makes it particularly attractive for international payments, where cross-border transactions often involve high costs and delays.
Several companies have embraced Bitcoin as a payment method. For instance, global brands like Microsoft, Tesla, and PayPal allow customers to use Bitcoin for purchases. In 2021, El Salvador made headlines by becoming the first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender, enabling its citizens to pay for goods, services, and even taxes using the cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning no single entity controls it. This reduces the risk of censorship and fraud. Bitcoin transactions are secured through blockchain technology, which ensures transparency and immutability. The transactions, particularly for international payments, are faster and cheaper compared to traditional systems. It provides access to financial services for unbanked populations, estimated to be over 1.7 billion people globally.
Despite its advantages, Bitcoin faces several challenges that hinder its widespread adoption. Bitcoin’s price is notoriously volatile, making it less appealing for everyday transactions. For instance, its value dropped from over $60,000 in 2021 to around $27,000 in early 2025. Governments worldwide have differing stances on Bitcoin, ranging from acceptance to outright bans. This uncertainty creates risks for users and businesses. Bitcoin mining requires substantial computational power, leading to criticism over its environmental impact. Bitcoin’s network can handle only a limited number of transactions per second, posing challenges for mass adoption.
The Future of Bitcoin
Despite these challenges, Bitcoin’s future remains promising. Its adoption is expected to grow as technology evolves and solutions to current limitations are developed. For instance, the Lightning Network, a second-layer solution, aims to improve Bitcoin’s scalability by enabling faster and cheaper transactions. Institutional interest in Bitcoin is also rising. Financial giants like BlackRock and Fidelity have introduced Bitcoin-related investment products, signaling confidence in its long-term potential. Moreover, central banks are exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), which could coexist with decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
As the global economy becomes increasingly digitized, Bitcoin is poised to play a pivotal role. Its potential to serve as a universal currency, independent of geopolitical boundaries, aligns with the demands of a connected world. Additionally, Bitcoin’s deflationary nature, due to its fixed supply, contrasts with the inflationary tendencies of fiat currencies, making it an attractive alternative for preserving wealth.
Bitcoin’s journey from an experimental digital asset to a contender for the title of “The New Gold” underscores its transformative impact on the financial landscape. While challenges remain, its growing adoption and integration into the global economy suggest a bright future. As Bitcoin continues to evolve, it represents more than just a speculative asset. It embodies the principles of financial sovereignty, decentralization, and innovation, paving the way for a new era of digital payments.
Whether it ultimately replaces or complements traditional systems, one thing is clear: Bitcoin is here to stay.