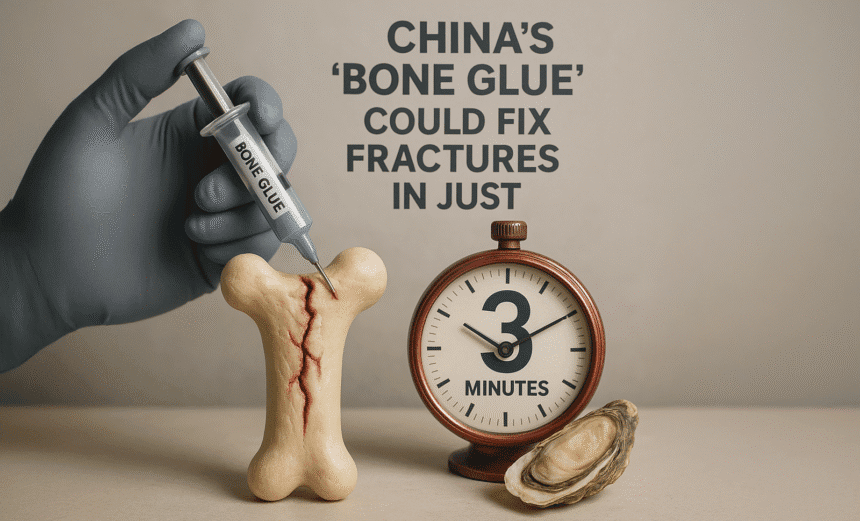
Imagine breaking a bone and having it repaired in the time while you scroll through Instagram reels? Perhaps this solution could have been found already. Chinese scientists in Zhejiang Province made that possible with Bone-02, a revolutionary bone adhesive inspired by oysters. Injected directly into a fracture, it could bond shattered bones within minutes, even in a blood-soaked surgical site, potentially replacing screws, plates, and hours in the operating room.
When Dr. Lin Xianfeng watched oysters cling firmly to a bridge underwater, he saw a solution to one of orthopedic surgery’s toughest challenges. Traditional fracture treatments often involve deep cuts to implant steel plates and screws, which can take hours and pose dangers such as infection, foreign-body responses, and post-operative problems. In contrast, Bone-02 can be injected directly into the fracture site, giving perfect repair almost instantly. In one trial, surgeons executed the treatment in less than three minutes, substantially decreasing surgical time and patient trauma.
Laboratory testing revealed the glue’s exceptional durability. Bone-02 has a maximum bonding force of about 400 pounds, a shear strength of around 0.5 MPa, and a compressive strength of nearly 10 MPa. These findings show that the glue could compete with or possibly replace traditional metal implants in a variety of fracture therapies. Another advantage is that the adhesive is biodegradable and will be absorbed by the body as the bone heals, eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove the implants.
The inspiration behind Bone-02 is quite fascinating as its medical potential. In 2016, Dr. Lin, then a resident physician, observed that even the most skilled surgeons struggled to achieve ideal results when fixing complex fractures. Reflecting on this challenge, he looked into nature for a solution. Watching oysters cling firmly to a bridge underwater sparked an idea to develop a bone adhesive capable of working in the human body’s moist, blood-rich environment. This observation laid the foundation for years of research, culminating in the creation of Bone-02.
Experts say the new adhesive could revolutionize orthopedic care, particularly in emergency and battlefield medicine, where rapid bone fixation is critical. It may also reduce healthcare costs by shortening operating times, lowering the risk of complications, and potentially minimizing the need for follow-up procedures.
While Bone-02 is still in the experimental and trial stages, clinicians and researchers are thrilled about its potential. “We believe this technology could fundamentally change how fractures are treated worldwide,” the doctor stated. The next steps will involve larger clinical trials to assess long-term safety, effectiveness, and possible applications in complex bone injuries.
Bone-02, with its combination of natural inspiration and cutting-edge research, demonstrates how studying nature can lead to life-changing medical breakthroughs. If this is widely adopted in the future, it might eliminate hours-long surgery, giving patients speedy recovery and fewer complications, which could potentially alter the field of orthopedic medicine forever.